Delving into the intricate world of haploid and diploid cells, this guide presents practice haploid v diploid worksheet answers that unravel the complexities of these fundamental biological concepts. Embark on an exploration of the distinct characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of haploid and diploid cells, delving into their implications for genetic diversity, adaptation, stability, and resilience.
Through engaging practice problems and real-world applications, this guide illuminates the significance of haploid cells in genetic research and medicine, while highlighting the crucial role of diploid cells in agriculture and genetic improvement. Prepare to enhance your understanding of haploidy and diploidy, unraveling the mysteries that lie within the very building blocks of life.
Haploid and Diploid Cells: Practice Haploid V Diploid Worksheet Answers
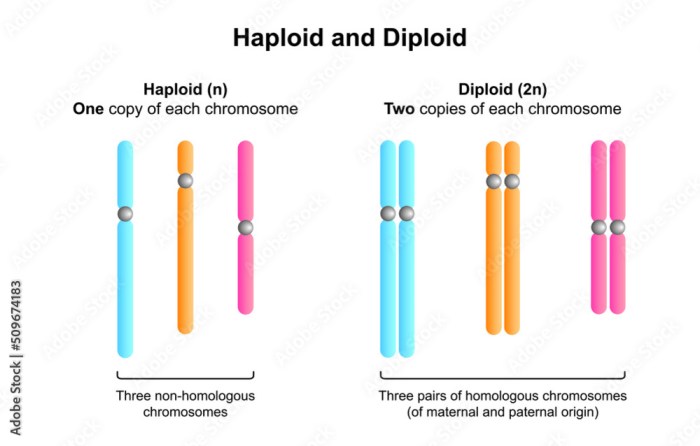
Haploid and diploid cells are two distinct types of cells that differ in their chromosome content. Understanding their differences is crucial for comprehending genetics and cellular biology.
1. Define Haploid and Diploid Cells
Haploid cells are cells that contain a single set of chromosomes, denoted as “n.” They are produced through meiosis, a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half. Diploid cells, on the other hand, contain two sets of chromosomes, denoted as “2n.”
They are formed through mitosis, a type of cell division that maintains the chromosome number.
Examples of organisms with haploid cells include gametes (eggs and sperm) and certain protists. Organisms with diploid cells include somatic cells (body cells) of humans, animals, and plants.
The difference in chromosome numbers between haploid and diploid cells is significant because it affects the genetic makeup and behavior of the cells.
2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Haploid and Diploid Cells
- Advantages of Haploid Cells:Genetic diversity, adaptation, and rapid reproduction
- Advantages of Diploid Cells:Genetic stability, resilience, and specialization
The trade-offs between haploid and diploid cells vary depending on the organism and its environment.
3. Practice Problems on Haploid and Diploid Cells
- Identify whether the following cells are haploid or diploid:
- Sperm cell
- Skin cell
- Egg cell
- Calculate the number of chromosomes in a diploid cell if the haploid chromosome number is 10.
- Explain the implications of haploidy in the life cycle of a fern.
4. Applications of Haploid and Diploid Cells
- Haploid Cells:Genetic research (mutagenesis, genetic mapping), biotechnology (haploid embryogenesis)
- Diploid Cells:Agriculture (hybrid vigor, genetic improvement), medicine (stem cell research, gene therapy)
The unique characteristics of haploid and diploid cells make them valuable for various applications in science and medicine.
5. Worksheet Answers for Practice Problems, Practice haploid v diploid worksheet answers
| Problem | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Identify whether the following cells are haploid or diploid:
|
|
|
| Calculate the number of chromosomes in a diploid cell if the haploid chromosome number is 10. | 20 | Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, so the number of chromosomes in a diploid cell with a haploid chromosome number of 10 is 10 x 2 = 20. |
| Explain the implications of haploidy in the life cycle of a fern. | Haploidy in ferns allows for genetic diversity through the alternation of generations. The haploid gametophyte produces gametes, while the diploid sporophyte produces spores. This cycle ensures genetic variation and adaptation to changing environmental conditions. |
Query Resolution
What is the primary distinction between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells possess a single set of chromosomes, while diploid cells possess two sets of chromosomes.
Explain the advantages of haploid cells.
Haploid cells facilitate genetic diversity through sexual reproduction and enable rapid adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Describe the trade-offs between haploid and diploid cells.
Haploid cells offer genetic diversity but lack genetic stability, while diploid cells provide genetic stability but limit genetic diversity.
Provide examples of organisms with haploid and diploid cells.
Sperm and egg cells are haploid, while somatic cells in the body are diploid.
