Embark on an intellectual odyssey with the Russian Revolution Worksheet Answer Key, an indispensable resource that unlocks the complexities of this pivotal historical event. Delve into the depths of pre-revolutionary Russia, unravel the catalysts that ignited the revolution, and witness the transformative events that shaped the course of history.
Through the lens of meticulous research and captivating storytelling, this guide illuminates the key players, timelines, and legacies of the Russian Revolution, leaving you with a profound understanding of its enduring impact on Russia and the global stage.
1. Historical Context
Prior to the revolution, Russia was an autocratic monarchy ruled by Tsar Nicholas II. The Tsar’s regime was characterized by political repression, economic inequality, and social stratification.
Economically, Russia was a predominantly agrarian society with a large peasantry. However, industrialization had begun to take hold in the late 19th century, leading to the emergence of a working class in urban centers.
Socially, Russian society was deeply divided. The aristocracy and wealthy landowners held most of the power and wealth, while the peasantry and working class lived in poverty and faced harsh conditions.
Tsar Nicholas II and His Government
Tsar Nicholas II was a weak and indecisive ruler. He was unable to effectively address the growing discontent within Russian society. His government’s policies, such as the Bloody Sunday massacre in 1905, further alienated the population.
2. Causes of the Revolution
The Russian Revolution was sparked by a combination of grievances and frustrations that had been building up for decades.
Key Grievances and Frustrations
- Political oppression and lack of civil liberties
- Economic inequality and poverty
- Social injustice and discrimination
Influence of Marxist Ideas and Revolutionary Movements
The ideas of Karl Marx and other socialist thinkers had a significant influence on the development of revolutionary movements in Russia.
Revolutionary organizations, such as the Bolsheviks and Mensheviks, emerged and played a key role in organizing and leading the revolution.
Impact of World War I
World War I placed a heavy burden on the Russian population. The war effort led to economic hardship, food shortages, and military defeats.
The war also exposed the weaknesses of the Tsarist regime and further undermined its legitimacy.
3. Key Events and Figures
The Russian Revolution was a complex and tumultuous period. The following is a timeline of some of the key events:
Timeline of Major Events
- 1905: Bloody Sunday massacre
- 1917: February Revolution, abdication of Tsar Nicholas II
- 1917: October Revolution, Bolshevik seizure of power
- 1918-1921: Russian Civil War
- 1922: Formation of the Soviet Union
Vladimir Lenin and Leon Trotsky, The russian revolution worksheet answer key
Vladimir Lenin was the leader of the Bolshevik Party and the first leader of the Soviet Union. He was a brilliant strategist and a charismatic orator.
Leon Trotsky was a prominent Bolshevik leader and military commander. He played a key role in the October Revolution and the Russian Civil War.
Significance of the October Revolution
The October Revolution was a turning point in Russian history. It marked the overthrow of the Tsarist regime and the establishment of the Soviet Union.
4. Impact and Legacy
The Russian Revolution had a profound impact on Russia and the world.
Immediate and Long-Term Consequences for Russia
- Overthrow of the Tsarist regime
- Establishment of the Soviet Union
- Implementation of a socialist economic system
- Industrialization and modernization
- Suppression of political dissent
Impact on International Relations and the Rise of Communism
The Russian Revolution inspired communist movements around the world.
It led to the formation of the Comintern, an international organization dedicated to promoting communism.
Lasting Legacy of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution continues to be a subject of debate and discussion.
Its legacy includes the establishment of the Soviet Union, the spread of communism, and the ongoing debate about the nature of revolution and social change.
5. Historiography and Interpretations: The Russian Revolution Worksheet Answer Key
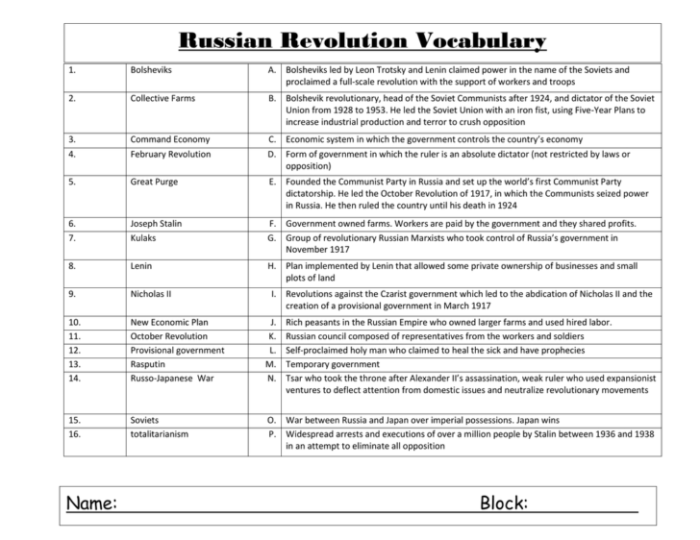
There are many different interpretations of the Russian Revolution.
Main Interpretations and Debates
- The Marxist interpretation emphasizes the economic and class factors that led to the revolution.
- The liberal interpretation focuses on the political and social factors that contributed to the revolution.
- The revisionist interpretation challenges the traditional view of the revolution as a necessary and inevitable event.
Different Perspectives on Lenin’s Role and the Nature of the Soviet Regime
Historians have different views on the role of Lenin in the revolution and the nature of the Soviet regime that he established.
Some historians view Lenin as a visionary leader who was committed to social justice, while others see him as a ruthless dictator who was responsible for the deaths of millions.
User Queries
What were the primary causes of the Russian Revolution?
Political oppression, economic inequality, and the social unrest fueled by World War I.
Who were the key figures in the Russian Revolution?
Vladimir Lenin, Leon Trotsky, and Tsar Nicholas II played pivotal roles.
What was the significance of the October Revolution?
It marked the overthrow of the provisional government and the establishment of the Soviet Union.