Introducing the Venn diagram of covalent and ionic bonds, a valuable tool that illuminates the intriguing characteristics of these fundamental chemical bonds. Covalent bonds, characterized by the sharing of electrons between atoms, and ionic bonds, formed through the transfer of electrons, exhibit unique properties that shape the behavior of molecules and compounds.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the similarities and differences between covalent and ionic bonds, providing a clear understanding of their nature and applications.
Covalent Bonds
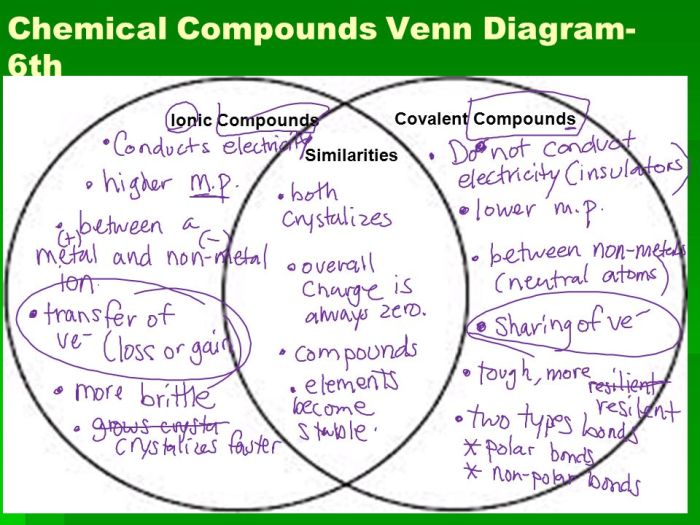
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, creating a strong bond. Covalent compounds are typically formed between non-metals and have properties such as low melting and boiling points, and poor electrical conductivity.
Polarity of Covalent Bonds, Venn diagram of covalent and ionic bonds
Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar. In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms. This creates a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other atom.
In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally between the two atoms.
Ionic Bonds
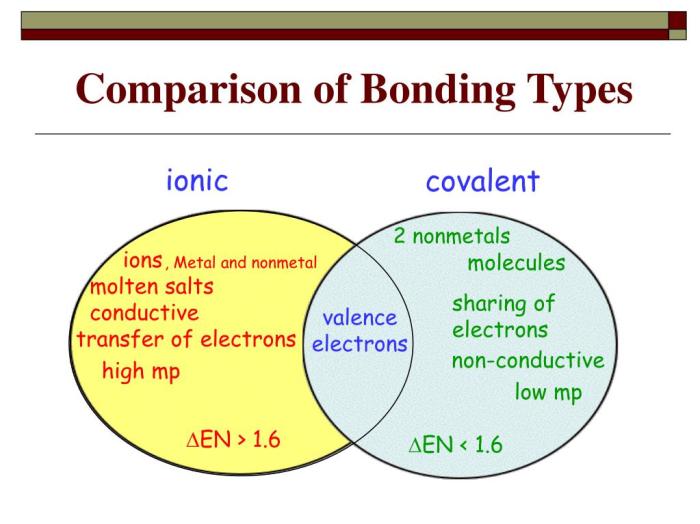
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that loses electrons becomes a positively charged ion, and the atom that gains electrons becomes a negatively charged ion. Ionic compounds are typically formed between a metal and a non-metal and have properties such as high melting and boiling points, and good electrical conductivity.
Solubility and Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are typically soluble in water and conduct electricity when dissolved in water. This is because the ions in the compound are free to move in water, allowing them to carry an electrical current.
Venn Diagram Comparison: Venn Diagram Of Covalent And Ionic Bonds

| Covalent Bonds | Ionic Bonds | |
|---|---|---|
| Similarities |
|
|
| Differences |
|
|
| Unique to Covalent Bonds |
|
|
| Unique to Ionic Bonds |
|
|
Real-World Applications
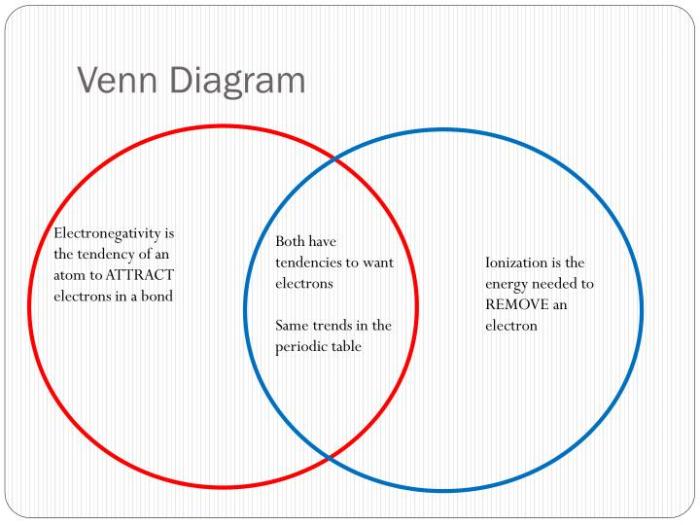
Covalent bonds are found in a wide variety of materials, including plastics, fuels, and DNA. Ionic bonds are found in a wide variety of materials, including salt, ceramics, and metals.
- Covalent bonds are used in the manufacture of plastics, which are used in a wide variety of products, from toys to car parts.
- Covalent bonds are also used in the manufacture of fuels, such as gasoline and natural gas.
- Ionic bonds are used in the manufacture of salt, which is used to flavor food and preserve food.
- Ionic bonds are also used in the manufacture of ceramics, which are used in a wide variety of products, from tiles to pottery.
- Ionic bonds are also used in the manufacture of metals, which are used in a wide variety of products, from cars to buildings.
Helpful Answers
What is the key difference between covalent and ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, while ionic bonds result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
Which type of bond is stronger, covalent or ionic?
Covalent bonds are generally stronger than ionic bonds due to the equal sharing of electrons.
What is the polarity of covalent bonds?
Covalent bonds can be nonpolar, polar, or highly polar depending on the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms.