Embark on a journey through the Covenants of the Bible Chart, a comprehensive guide that unravels the intricate tapestry of agreements between God and humanity. From the seminal covenants of the Old Testament to the transformative covenant of the New Testament, this chart provides a captivating overview of the divine promises and obligations that have shaped the course of history.
Through a meticulous examination of biblical covenants, we will explore their types, significance, and enduring impact on Christian faith and practice. Prepare to delve into a realm where divine encounters and human responses intertwine, shaping the destiny of individuals and nations.
Overview of Covenants in the Bible
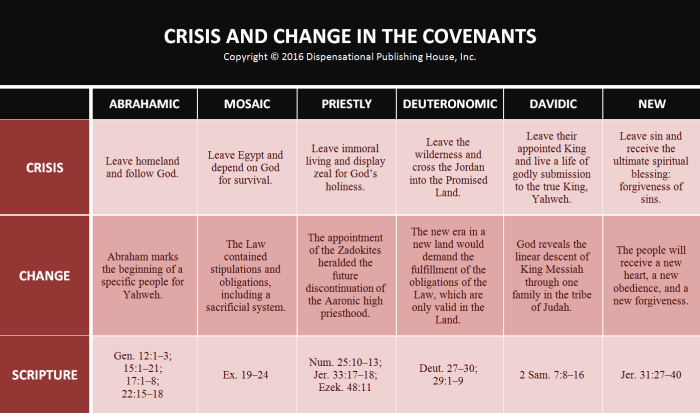
Covenants play a crucial role in the narrative of the Bible, establishing relationships and obligations between God and humanity, as well as within human societies. These covenants serve as agreements or contracts, often accompanied by specific promises, conditions, and consequences.
Examples of Significant Covenants
Throughout the Bible, several significant covenants are mentioned, each marking a pivotal moment in the relationship between God and his people:
- Covenant with Noah:After the great flood, God establishes a covenant with Noah, promising never to destroy the earth by water again and establishing the rainbow as a sign of this covenant (Genesis 9:8-17).
- Covenant with Abraham:God enters into a covenant with Abraham, promising to make him a great nation, bless his descendants, and give them the land of Canaan (Genesis 12:1-3, 15:18-21).
- Covenant with Moses:God gives the Ten Commandments and establishes a covenant with the Israelites at Mount Sinai, outlining their obligations and his promises of blessing and protection (Exodus 19-24).
- New Covenant:Jesus Christ, as the Messiah, initiates a new covenant with believers, offering forgiveness of sins, the indwelling of the Holy Spirit, and eternal life (Jeremiah 31:31-34, Hebrews 8:6-13).
Purpose and Significance of Covenants
Covenants serve several purposes and hold great significance in the biblical narrative:
- Establish Relationships:Covenants create a formal and binding relationship between God and individuals or groups, outlining their respective roles and responsibilities.
- Convey Promises and Blessings:God’s covenants often include promises of blessings, protection, and favor to those who remain faithful to the terms of the agreement.
- Define Obligations and Consequences:Covenants also specify the obligations and responsibilities of the parties involved, along with the consequences for breaking the covenant.
- Reveal God’s Character:Through covenants, God reveals his faithfulness, mercy, and desire for relationship with humanity.
Types of Covenants
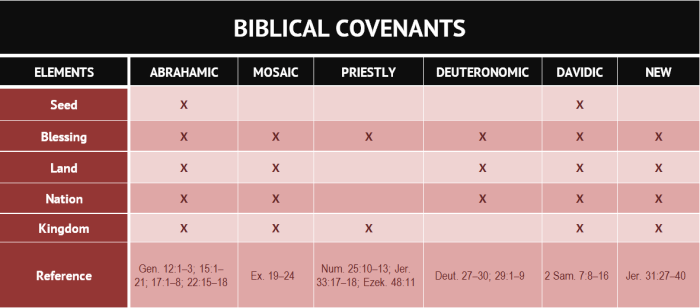
Covenants in the Bible are diverse, each with unique characteristics and purposes. Understanding these types helps us grasp the multifaceted nature of God’s relationships with humanity.
Unconditional Covenants
Unconditional covenants are promises made by God without any conditions attached. They are based solely on God’s grace and faithfulness.
- Noahic Covenant:God promised never to destroy the earth by flood again (Genesis 9:8-17).
- Abrahamic Covenant:God promised to bless Abraham and his descendants, making them a great nation (Genesis 12:1-3).
Conditional Covenants
Conditional covenants are agreements that require obedience from the human party. God promises blessings for obedience and consequences for disobedience.
- Mosaic Covenant:God gave the Ten Commandments and other laws to the Israelites, promising blessings for obedience and curses for disobedience (Exodus 19-24).
- Davidic Covenant:God promised David that his dynasty would rule forever (2 Samuel 7:8-16).
New Covenant
The New Covenant is the culmination of God’s covenant relationships with humanity. It is based on the sacrifice of Jesus Christ and offers forgiveness of sins and eternal life.
- Jeremiah’s Prophecy:God promised a new covenant that would be written on the hearts of his people (Jeremiah 31:31-34).
- Fulfillment in Jesus:Jesus inaugurated the New Covenant through his death and resurrection (Matthew 26:28).
These covenant types demonstrate the variety of ways God has interacted with humanity throughout history. They reveal his faithfulness, grace, and the importance of obedience in our relationship with him.
Charting Covenants
To summarize the key covenants of the Bible, we can create a comprehensive table. This table will provide an overview of each covenant, including its name, the parties involved, its provisions, and its significance.
By presenting this information in a structured format, we can easily compare and contrast the different covenants and gain a deeper understanding of their role in the biblical narrative.
Table of Covenants
| Covenant Name | Parties Involved | Provisions | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adam and Eve Covenant | God, Adam, and Eve | Obedience to God’s command | Established the relationship between God and humanity |
| Noahic Covenant | God and Noah | God’s promise not to destroy the earth by flood | Established God’s covenant with all living creatures |
| Abrahamic Covenant | God and Abraham | God’s promise to make Abraham a great nation | Established the nation of Israel and the promise of a Messiah |
| Mosaic Covenant | God and the Israelites | The Ten Commandments and other laws | Established the law as a guide for the Israelites |
| Davidic Covenant | God and David | God’s promise to establish David’s throne forever | Established the Davidic dynasty and the promise of a Messiah from David’s line |
| New Covenant | God and believers in Jesus Christ | Forgiveness of sins and the indwelling of the Holy Spirit | Established a new relationship between God and humanity through Jesus Christ |
Biblical Examples
The Bible contains numerous examples of covenants between God and individuals, groups, or nations. These covenants illustrate the principles of covenants and their historical and theological significance.
Covenant with Abraham
God established a covenant with Abraham, promising him descendants as numerous as the stars in the sky and land in Canaan. This covenant was a foundational event in the history of Israel, establishing God’s faithfulness and Abraham’s obedience.
For a comprehensive understanding of biblical covenants, consider exploring the words with f o s s i l in the Old and New Testaments. These words provide insights into the nature of God’s agreements with humanity, illuminating the significance of covenants in shaping our relationship with Him.
Covenant with Moses, Covenants of the bible chart
God made a covenant with Moses at Mount Sinai, giving him the Ten Commandments and establishing the Law as a guide for Israel’s conduct. This covenant defined the relationship between God and his people, shaping their social, religious, and ethical life.
Covenant with David
God established a covenant with David, promising that his dynasty would rule forever. This covenant ensured the continuity of God’s presence among his people and became a source of hope and expectation for future generations.
New Covenant
Jesus Christ established a new covenant through his death and resurrection. This covenant is based on grace and forgiveness, offering salvation to all who believe in him. The New Covenant transforms the relationship between God and his people, offering a personal and intimate connection with God.
Implications for Christian Faith
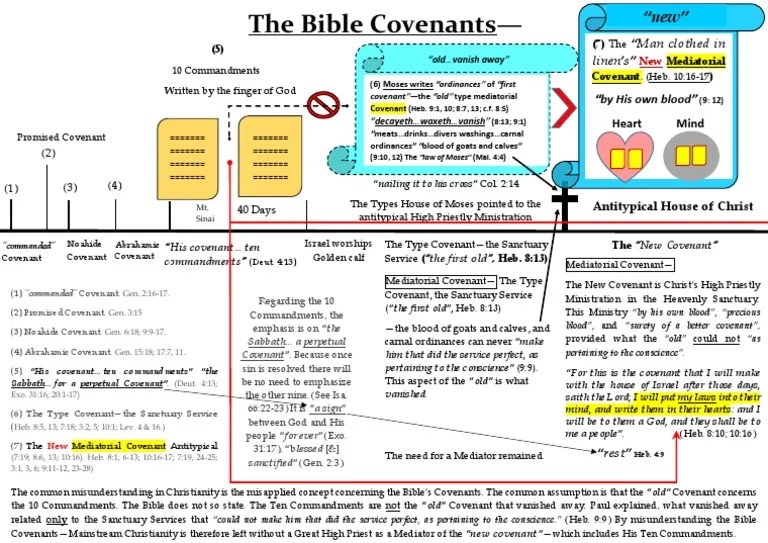
The covenants of the Bible provide a framework for understanding the relationship between God and humanity. They reveal God’s plan of salvation, redemption, and the establishment of a covenant relationship with his people.
Role of Covenants in Salvation and Redemption
The covenants of the Bible play a crucial role in the salvation and redemption of humanity. The covenant with Abraham established the promise of a Messiah who would bring blessing to all nations. The covenant with Moses provided a way for Israel to experience forgiveness and reconciliation with God through the sacrificial system.
The covenant with David established a dynasty that would culminate in the Messiah, Jesus Christ. Through his death and resurrection, Jesus fulfilled the covenants and became the mediator of a new covenant, the New Covenant, which offers forgiveness of sins, eternal life, and a restored relationship with God.
Practical Implications of Covenant Understanding
Understanding the covenants of the Bible has practical implications for Christian faith. It helps us to:
- Appreciate the faithfulness of God and his commitment to his people.
- Recognize the importance of obedience and faithfulness in our own lives.
- Trust in God’s promises and live in hope of their fulfillment.
- Live in covenant relationship with God, characterized by love, trust, and obedience.
- Share the message of salvation and redemption with others.
Covenants and Christian Living
Covenants provide a profound framework for understanding our relationship with God and guiding our daily lives. They reveal principles that foster faithfulness, obedience, and commitment, shaping our journey as Christians.
Faithfulness to God’s covenant requires unwavering trust and obedience to His commandments. By keeping our vows, we honor the bond we share with Him and demonstrate our love and commitment.
Obedience and Commitment
Covenants demand obedience to God’s will and a willingness to align our actions with His principles. This obedience is not merely external compliance but a heartfelt desire to live in harmony with God’s purpose for our lives.
Commitment to the covenant implies enduring loyalty and steadfastness, even in challenging times. It involves a willingness to sacrifice our own desires and priorities to uphold the covenant’s terms.
Examples in Daily Life
- Honoring our baptismal vows by living a life that reflects our commitment to Christ.
- Practicing forgiveness and reconciliation in relationships, following the example of God’s covenantal love.
- Seeking God’s guidance in decision-making, acknowledging our dependence on His wisdom and direction.
Historical Impact: Covenants Of The Bible Chart
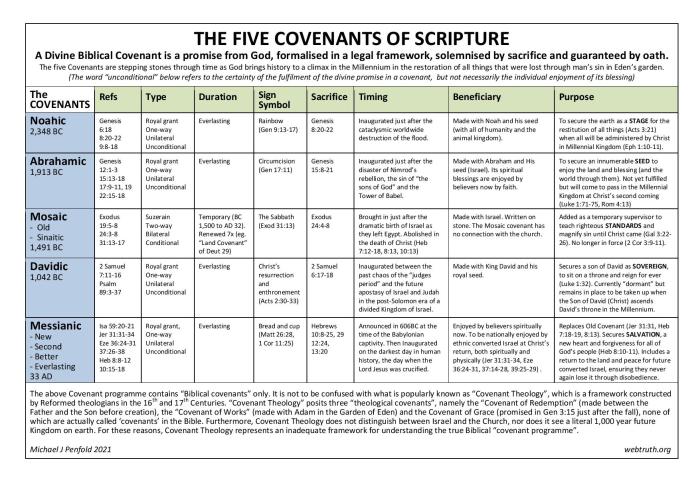
The biblical covenants have left an enduring mark on societies and cultures throughout history. These covenants have shaped laws, social structures, and religious beliefs, influencing the course of human civilization.
The covenant between God and Abraham, for instance, established the concept of a chosen people and laid the foundation for the development of Judaism. The covenant between God and Israel at Mount Sinai provided a comprehensive legal and moral framework that shaped the laws and social customs of ancient Israel.
Laws and Social Structures
- Biblical covenants often included detailed laws and regulations that governed various aspects of society, from criminal justice to family life. These laws provided a framework for social order and stability.
- For example, the Ten Commandments, given as part of the covenant at Mount Sinai, established fundamental moral principles that have influenced legal systems and ethical codes in many cultures.
Religious Beliefs
- Covenants played a central role in the development of religious beliefs and practices. The covenant between God and Abraham established the worship of the one true God, while the covenant with Israel provided a framework for religious rituals and ceremonies.
- The concept of a covenant between God and humanity has also influenced other major world religions, such as Christianity and Islam.
Legacy and Influence
The legacy of biblical covenants continues to shape human history. The principles of justice, mercy, and compassion enshrined in these covenants have inspired social movements and reforms.
Moreover, the concept of a covenant relationship between God and humanity has provided a source of hope and guidance for countless individuals and communities throughout the ages.
Q&A
What is the significance of covenants in the Bible?
Covenants in the Bible represent binding agreements between God and humanity, establishing mutual obligations and promises. They reveal God’s plan for redemption, salvation, and the establishment of his kingdom on earth.
How many types of covenants are there in the Bible?
The Bible presents various types of covenants, including the Abrahamic Covenant, the Mosaic Covenant, the Davidic Covenant, and the New Covenant. Each covenant has unique characteristics and played a specific role in God’s unfolding plan.
What is the purpose of the Covenants of the Bible Chart?
The Covenants of the Bible Chart provides a concise and organized overview of the key covenants found in Scripture. It serves as a valuable resource for understanding the historical context, provisions, and significance of these agreements, aiding in a deeper comprehension of biblical theology.